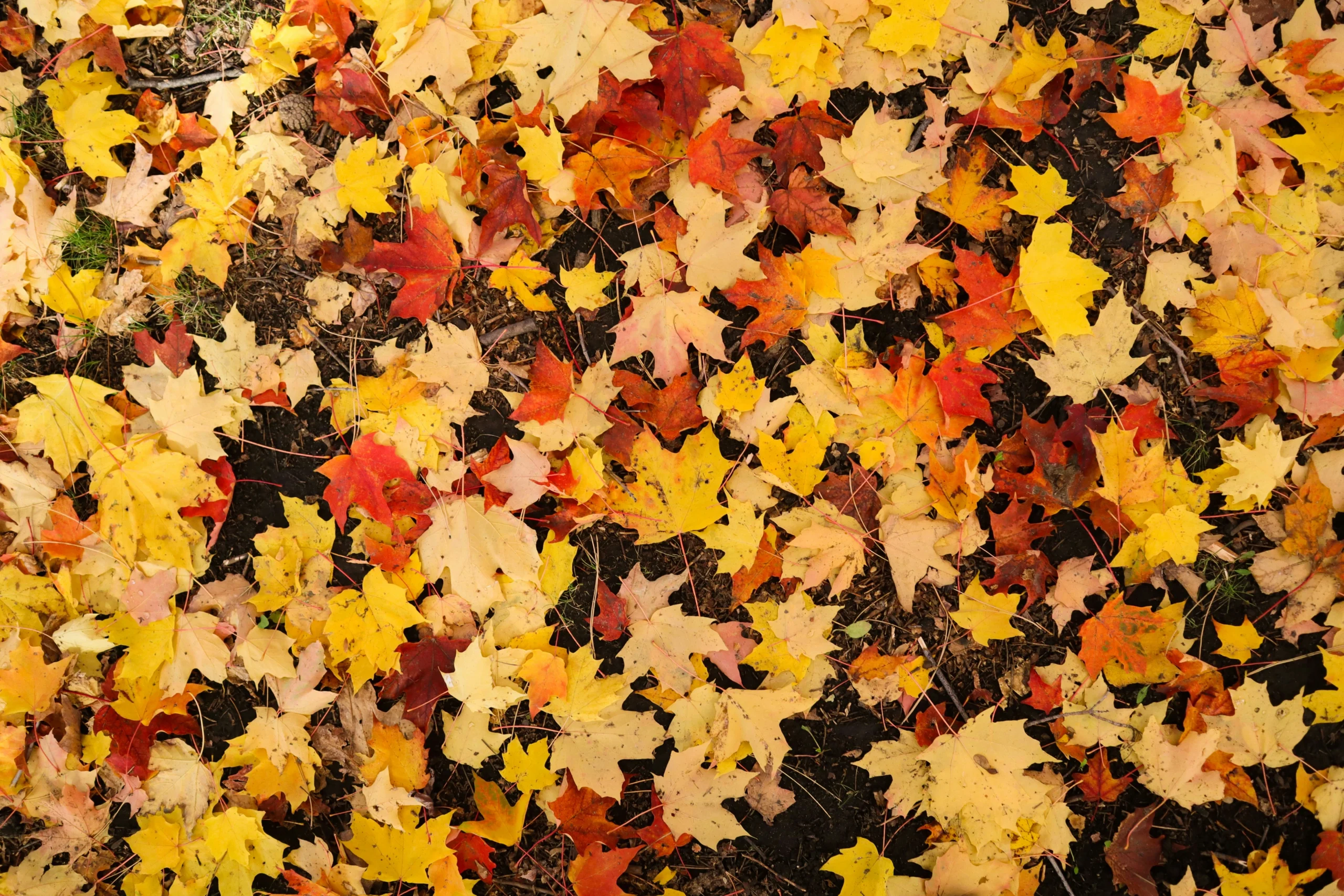
Canada is known for its diverse natural landscapes, from snow-capped mountains to vast boreal forests. Yet, one symbol stands out in both the country’s flag and its natural heritage: the maple tree. In 1996, Canada officially designated the maple as its national tree, solidifying its importance not only in Canadian ecology but also in the country’s culture and economy.
The maple tree, particularly the sugar maple (Acer saccharum), is a powerful symbol of the nation. It is embedded in the Canadian identity, representing strength, resilience, and the interconnectedness of Canada’s natural environment and its people. In this article, we will explore the historical, cultural, and ecological significance of the maple tree and why it holds such a prominent place in Canadian society.
The History of the Maple in Canada
The connection between the maple tree and Canada dates back centuries. Indigenous peoples across the country were the first to recognize the value of the maple tree, particularly for its sap, which could be harvested and processed into maple syrup. This syrup became an important staple in Indigenous diets and held cultural significance in many Indigenous communities.
When European settlers arrived in North America, they quickly learned the art of maple syrup production from the Indigenous peoples. Over time, this practice evolved, and maple syrup became one of Canada’s most iconic exports. By the 19th century, maple syrup production had become a significant industry in Canada, and it remains a key part of the country’s agricultural economy today.
Canada produces about 70-80% of the world’s maple syrup, and the vast majority of this comes from the province of Quebec, where the sugar maple thrives. The tree’s sap is collected in the spring when the temperature fluctuations between day and night cause the sap to flow. This sap is then boiled down to produce the golden syrup that is enjoyed worldwide.
The Maple as a Symbol of Canada
The maple tree’s symbolic importance to Canada is immense. Most notably, the maple leaf is featured at the center of Canada’s national flag, which was adopted in 1965. The leaf is a symbol of Canada’s natural beauty, heritage, and unity. It represents the vast forests that stretch across the country and the strong connection between Canadians and their environment.
The adoption of the maple leaf as the centerpiece of the flag was not just an aesthetic choice but a reflection of Canadian values. The maple leaf represents Canada’s diversity, as the tree is found across the country, from coast to coast. The symbolism of the leaf is intertwined with the Canadian identity, evoking images of autumn, the changing of seasons, and the richness of the country’s forests.
Beyond the flag, the maple tree has become a national symbol of strength and endurance. Like the sturdy maple, Canadians are seen as resilient and adaptable people who thrive in a harsh but beautiful environment. The maple tree also represents the interconnectedness of nature and people, with the sap of the tree nourishing Canadians both literally and culturally through the production of maple syrup.
The Maple Tree’s Role in Canada’s Economy
The maple tree plays an important role in Canada’s economy, particularly through the production of maple syrup. Canada is the world’s largest producer of maple syrup, and this industry is a major economic contributor, particularly in Quebec, Ontario, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia.
In 2022, the Canadian maple syrup industry generated over $400 million in revenue, with the majority of the syrup produced being exported to the United States and around the world. Quebec alone accounts for approximately 70% of the global maple syrup supply. The syrup is a significant agricultural product, and the maple syrup harvest season in Canada is a celebrated event.
Beyond syrup production, the maple tree also contributes to Canada’s forestry industry. The wood of the maple tree is highly valued for its strength and durability and is used to produce furniture, flooring, and even musical instruments. The wood’s dense grain makes it ideal for crafting fine furniture and cabinetry, and it’s a sought-after material in both domestic and international markets.
The Ecological Significance of the Maple Tree
The maple tree, especially the sugar maple, plays a crucial role in Canada’s ecosystems. It is an important component of temperate forests across the country, providing habitat and sustenance for a variety of wildlife. The sugar maple, in particular, is known for its beautiful fall foliage, which attracts tourists and nature lovers from around the world.
In addition to its aesthetic value, the maple tree provides important ecological services. The dense canopy of maple trees helps maintain biodiversity by creating shaded areas that support a variety of plant and animal species. The tree’s leaves also play a role in soil health, contributing organic matter that enriches the ground beneath them.
Maple trees are also an important part of Canada’s carbon cycle. Like all trees, they absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen, helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change. In urban areas, maples are often planted to provide shade, reduce heat, and improve air quality.
Maple Syrup: A Cultural Staple
The production of maple syrup is an integral part of Canadian culture. The tradition of maple syrup tapping dates back centuries and continues to be a key aspect of Canadian life, particularly in rural communities. The arrival of spring and the maple syrup season is celebrated in many parts of the country with festivals, events, and gatherings.
The “sugaring-off” season is a beloved time when families and communities come together to harvest sap and produce syrup. It is common for Canadians to visit sugar shacks, where they can watch the syrup-making process and sample the fresh product. This practice is so ingrained in Canadian culture that it is often considered a rite of passage for children to help tap maple trees and learn the traditional methods of syrup production.
The Future of the Maple Tree in Canada
As climate change and environmental challenges continue to affect ecosystems worldwide, the maple tree faces potential risks. Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns could alter the timing of sap flow and impact the health of maple forests. Researchers are working to understand how the maple tree might adapt to these changes and ensure the continued success of maple syrup production.
In the face of these challenges, Canadians remain committed to protecting their natural heritage, including the iconic maple tree. Conservation efforts are underway to preserve maple forests, and sustainable practices are being implemented to protect the health of these trees for future generations.
Conclusion
The maple tree, particularly the sugar maple, is an enduring symbol of Canada’s natural beauty, culture, and heritage. Its role in Canadian history, its cultural significance, and its contributions to the economy make it an essential part of the country’s identity. From the production of maple syrup to its ecological importance, the maple tree remains a symbol of resilience, strength, and interconnectedness.
As Canada continues to navigate environmental and societal challenges, the maple tree will remain a reminder of the country’s deep connection to nature and the enduring values that define Canadian society.
At Canadian Updates, we are committed to bringing you stories that reflect the heart of Canadian heritage, culture, and identity, just as the maple tree stands as a symbol of these timeless values.